Figure 5. Seesaw analogy.VPT
2. The analogy of a school dance can be used to illustrate many gas
relationships. If you increase the size of the room (volume), the
pressure of dancers decreases.
1. Use plastic ruler. Hang sign indicating temperature (T) in middle. Show that if T is constant, see-saw effect takes place and P is inversely proportional to V. If V is held constant, increasing P, increases T, etc.Pictures in the Mind
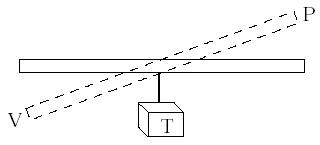
Figure 5. Seesaw analogy.VPT2. The analogy of a school dance can be used to illustrate many gas relationships. If you increase the size of the room (volume), the pressure of dancers decreases.
The study of gases provides a good example of relationships among variables and the identification of variables and constants. It also provides excellent opportunities to create “pictures in the mind.”General Questions
1. Predict what will happen as you change certain conditions of gases, holding other conditions constant (see Tips for the Teacher ).2. How can you determine the molar mass of a gaseous substance? [If you measure the mass of a sample of gaseous substance at a known temperature, pressure, and volume, it is possible to determine the molar mass using the general gas law, PV = nRT. Using the known temperature, pressure, and volume, the amount (moles) of gas can be calculated. The measured mass divided by the amount of gas provides the molar mass. See Tips for the Teacher for further explanation.]
3. What is an ideal gas? [One in which the molecules occupy no volume and in which there are no attractions among molecules. Of course this is an ideal, not a real, situation, but real gases at room temperature and standard atmospheric pressure (1 atm) can behave nearly ideally since their molecules are so far apart. When gases are under high pressure and low temperature, their molecules come closer together and no longer act ideally.]
4. Why is it necessary to change the temperature scale to kelvins in applications of gas laws? [So that “zero” on the temperature scale represents the lowest possible temperature. With such a temperature scale, ideal gas volume is directly proportional to temperature.]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|