 Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index
Name ________________________
AP Chemistry By Satellite
John I. Gelder
Exam IV
May 11, 1992
![]()
INSTRUCTIONS:
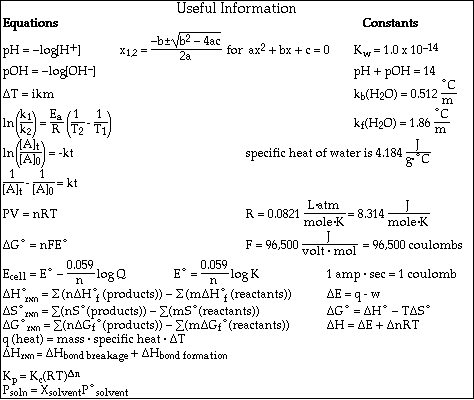
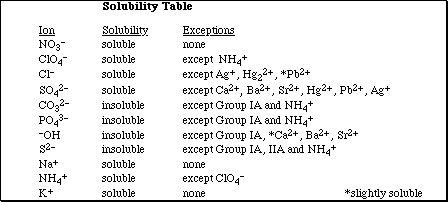
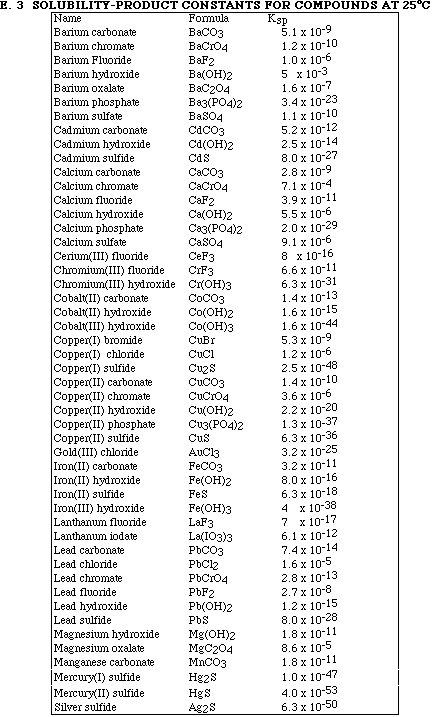
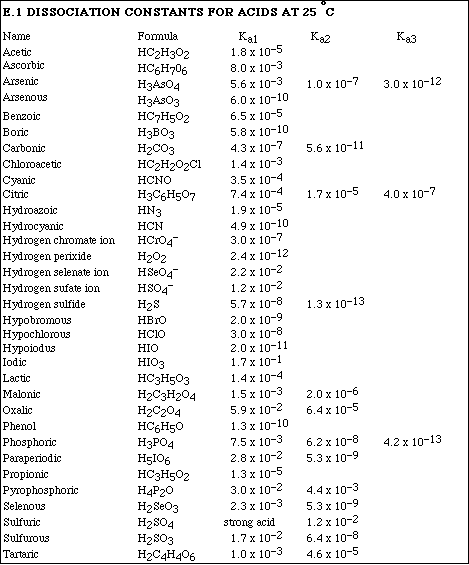
1. This examination consists of a total of 8 different pages. The last 2 pages include important mathematical equations and constants, a solubility table, a periodic table, and a table standard reduction potentials. All work should be done in this booklet.
2. PRINT your name, high school, teaching partner's name and today's date now in the space at the top of this sheet. DO NOT SEPARATE THE PAGES.
3. Answer all questions that you can and whenever called for show your work clearly. Your method of solving problems should pattern the approach used in lecture. You do not have to show your work for the multiple choice or short answer questions.
4. No credit will be awarded if your work is not shown in problem 2 - 7. Please circle your final answer!
5. Point values are shown next to the problem number.
6. Budget your time for each of the questions. Some problems may have a low point value yet be very challenging. If you do not recognize the solution to a question quickly, skip it, and return to the question after completing the easier problems.
7. Look through the exam before beginning; plan your work; then begin.
![]()
8. Relax and do well.
![]()

APCBS Exam IV 2
(12) 1. Complete and balance the following reactions. Identify all product's phases as either (g)as, (l)iquid, (s)olid or (aq)ueous. If no reaction occurs, write NR.

(18) 2. Balance the following oxidation-reduction reactions using the half-reaction method.

identify the oxidizing agent CO32- identify the reducing agent N 2H4(aq)

identify the oxidizing agent Hg2HPO4(s)
![]() identify the reducing agent Au(s)
identify the reducing agent Au(s)
APCBS Exam IV 3
(8) 3. Write the half-reactions and determine Eº for the electrochemical cells as described below, in part b include the overall chemical equation.

b. Ni(s) | Ni2+(aq) || Cl2(g), Cl-(aq) | Pt(s)

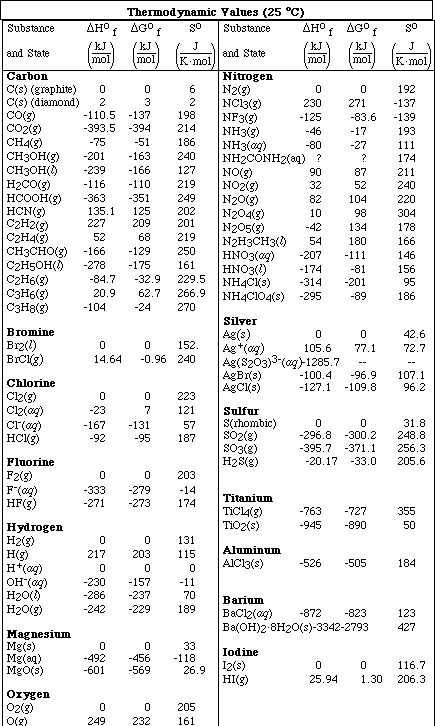
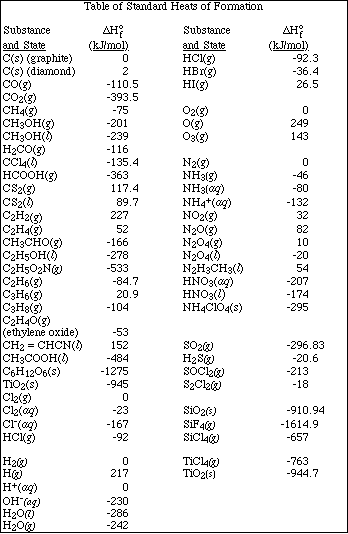
(14) 4. Given the following data

a. Using the above data, calculate DGº, DSº, and DHº for the reaction,
![]()

b. Determine at what temperature is the reaction spontaneous.

APCBS Exam IV 4
![]()
(8) 5. A voltaic cell is constructed to carry out the reaction,
![]()
If the [Cr3+] = 0.0300 M, [Pb2+] = 0.150 M and the [Cr2+] = 0.250 M, calculate Ecell at 25 ºC.

(8) 6. Calculate K and DGº for the reaction in Problem #5.

APCBS Exam IV 5
(12) 7. A voltaic cell consists of an anode compartment with a nickle electrode immersed in a NiSO4 solution and a cathode compartment with a copper electrode immersed in a CuSO 4 solution. A salt bridge connects the two cells.
a. Write a balanced equation for the cell reaction.
![]()
b. A current of 1.50 amps is observed to flow for a period of 2.00 hours. How much charge passes through the circuit during this time? How many moles of electrons is this charge equivalent to?
![]()
![]()
c. Calculate the change in mass at the copper electron.
![]()
d. Calculate the change in mass at the nickle electrode.
![]()
e. At which of the two electrodes does the mass increase?
mass increases at the cathode
APCBS Exam IV 6
(8) 8. Write the half-reactions which occur at each electrode when the following solutions are electrolyzed between inert electrodes. If more than one half-reaction can occur at the anode or cathode, write all possible half-reactions and briefly explain which half-reaction will occur.
a. AlCl3(l)
ANODE:
![]()
CATHODE:
![]()
b. CuBr2(aq)
ANODE:
![]()
CATHODE:
![]()
Short Answer: (12 points)
9. Which of the following species is the strongest reducing agent? (Circle your answer.)
![]()
10. Will Sn(s) displace Ag+(aq) from solution?
YES
11. Will gold dissolve in HCl(aq) ?
NO
![]()
12. From the following information estimate the Eº for
![]()
![]()
knowing the metal, M, dissolves in 1 M HCl. It will displace Fe2+(aq), but not Al3+(aq).
![]()
Mn or Zn