 Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index
Name ________________________
AP Chemistry By Satellite
John I. Gelder
Exam IV
December 4, 1990
![]()
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. This examination consists of a total of 8 different pages. The last page include a periodic table and some useful information. All work should be done in this booklet.
2. PRINT your name, high school, teaching partner's name and the date now in the space at the top of this sheet. DO NOT SEPARATE THESE PAGES.
3. Answer all questions that you can and whenever called for show your work clearly. Your method of solving problems should pattern the approach used in lecture. You do not have to show your work for the multiple choice or short answer questions.
4. No credit will be awarded if your work is not shown in problems 5, 6, 8 and 9.
5. Point values are shown next to the problem number.
6. Budget your time for each of the questions. Some problems may have a low point value yet be very challenging. If you do not recognize the solution to a question quickly, skip it, and return to the question after completing the easier problems.
7. Look through the exam before beginning; plan your work; then begin.
![]()
8. Relax and do well.
![]()
APCBS Exam IV PAGE 2
![]()
(12) 1. Draw a Lewis electron-dot structure for each of the covalent molecules below. Include all resonance
structures if they are needed to adequately represent the bonding in the molecule.
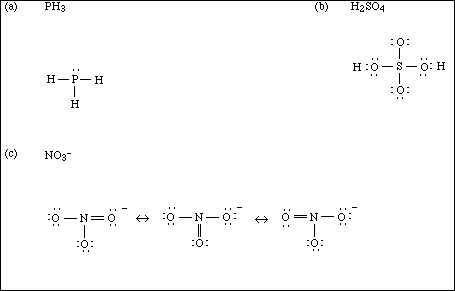
![]()
(15) 2. Complete the following table
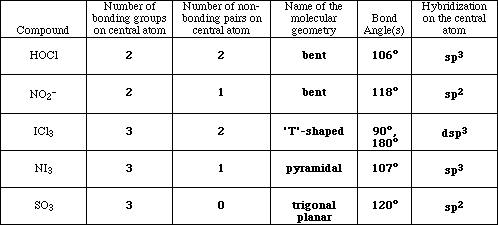
APCBS Exam IV PAGE 3
![]()
(5) 3. Which of the molecules list in Problem #2 are polar and which are nonpolar?

(5) 4. Explain why I3- ion is linear.

![]()
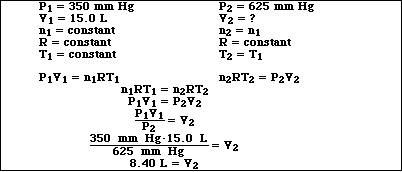
(9) 5. A sample of an ideal gas initially has a volume of 15.0 L at 350 mmHg. Calculate the new volume if the
pressure is changed to 625 mmHg. Assume the temperature and quantity of gas are held constant.
![]()
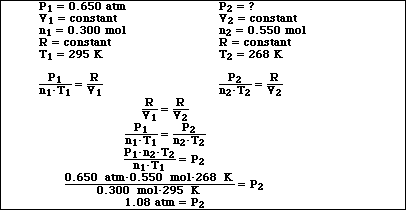
(8) 6. A flask contains 0.300 moles of CO2 at 22 ºC and 0.650 atm. If 0.250 moles of CO2 are added to the
flask and the temperature lowered to -5 ºC, calculate the new pressure.
APCBS Exam IV PAGE 4
![]()
(8) Solve ONE of the two problems on this page. (A second problem will not be scored.)
7. In Experiment 7: Charles Law the length of a column of air was measured at different temperatures.
This data was plotted and a value for absolute zero was determined.
a) If Charles Law is the relationship between absolute temperature and the volume of a gas, explain
why in this experiment a length of gas was measured instead of a volume of a gas.
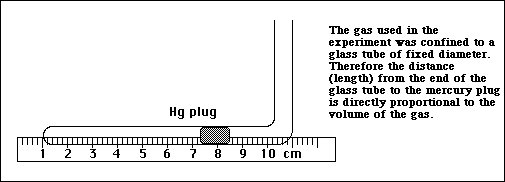
b) How was the value of absolute zero determined when the data collected ranged from near 0 ºC to
near 90 ºC?
The data collected between 0 ºC and 90 ºC was plotted on a graph with the
distance (length) from the end of the glass tube to the mercury plug plotted on the y -
axis and temperature on the x-axis. The best straight line through this data was
extended to point on the x-axis at which y = 0. This is the temperature at which the
volume of the gas in the glass tube equals zero, or absolute zero.
8. Below is a set of data from Experiment 8: Molecular Weight of a Volatile Liquid;
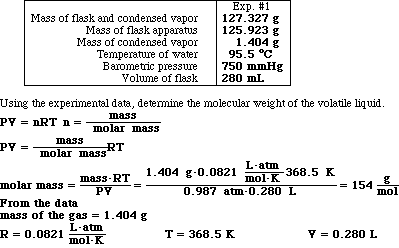 P = 750 mm Hg
P = 750 mm Hg
![]() = 0.987 atm
= 0.987 atm
APCBS Exam IV PAGE 5
![]()
(8) 9. A laboratory preparation for oxygen gas which was once commonly used is described by the reaction
![]()
![]()
Calculate the volume of O2 gas at 23 ºC and 750 mmHg which could be collected from the complete
decomposition of 24.5 g of KClO3.
![]()
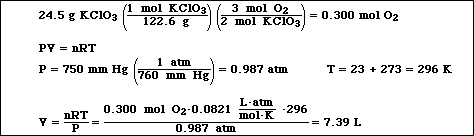
![]()
(8) 10. The pressure of a fixed quantity of gas at constant volume decreases as the temperature of the container
decreases. Explain this observation in terms of the kinetic molecular theory.
Pressure is a result of the collisions of the gas particles with the walls of the container. If the temperature is lowered, the average kinetic energy of the particles decreases, resulting in a decrease in the velocity of the gas particles. Slow moving gas particles collide with the walls of the container with lower frequency and with less momentum. The net effect is a corresponding drop in the pressure of the gas in the container.
![]()
(5) 11. What is the hybridization on each of the designated central atoms in the molecule shown below.
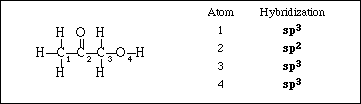
APCBS Exam IV PAGE 6
![]()
Multiple Choice:
Print the letter (A, B, C, D, E) which corresponds to the answer selected.
12. C ![]() 13. D
13. D ![]() 14. E
14. E ![]() 15. B
15. B ![]() 16. C
16. C
ONLY THE ANSWERS IN THE AREA ABOVE WILL BE GRADED. Select the most correct answer for each question. Each question is worth 3 points.
12. The fact that there is a liquid state is contrary to the postulate of the Kinetic Molecular Theory which states
A) gases are composed of molecules
B) collisions of molecules are elastic
C) there are no attractive forces between molecules
D) molecules are in constant, random, motion
E) kinetic energy is proportional to the absolute temperature
13. Which of the following graphs does not represent the behavior of an ideal gas?
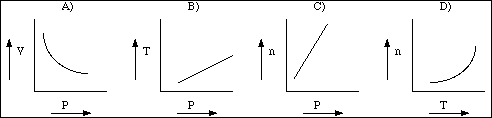
14. Which of the following molecules does not contain a p-bond?
![]()
A) HCN
B) CO2
C) C2H2
D) N2
E) OF2
15. Hydrogen gas is collected over water at 24 ºC. The total pressure of the sample is 748 mmHg. At 24 ºC, the vapor pressure of water is 22 mmHg. What is the partial pressure of hydrogen gas?
A) 22 mmHg
B) 726 mmHg
C) 748 mmHg
D) 760 mmHg
E) 770 mmHg
APCBS Exam IV PAGE 7
![]()
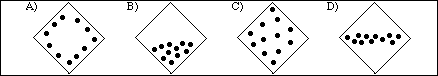
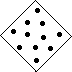
16. The following diagram represents a cross-section area of a pipe used to transport natural gas, N2
(nitrogen), at 25 ºC and 2.5 atm pressure. (The dots represent the distribution of nitrogen molecules.)
![]()
![]()
Which of the following diagrams illustrates the distribution of N2 molecules in the pipe if the temperature
is lowered to -35 ºC?