 Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index
Name ________________________
AP Chemistry By Satellite
John I. Gelder
Exam I
February 7, 1991
![]()
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. This examination consists of a total of 9 different pages. The last page includes important mathematical equations, a periodic table, and a table of vapor pressures for water. All work should be done in this booklet.
2. PRINT your name, high school, teaching partner's name and today's date now in the space at the top of this sheet. DO NOT SEPARATE THE PAGES.
3. Answer all questions that you can and whenever called for show your work clearly. Your method of solving problems should pattern the approach used in lecture. You do not have to show your work for the multiple choice or short answer questions.
4. No credit will be awarded if your work is not shown in problem 1 - 7. Please circle your final answer!
5. Point values are shown next to the problem number.
6. Budget your time for each of the questions. Some problems may have a low point value yet be very challenging. If you do not recognize the solution to a question quickly, skip it, and return to the question after completing the easier problems.
7. Look through the exam before beginning; plan your work; then begin.
![]()
8. Relax and do well.
![]()
CBS Exam I PAGE 2
![]()
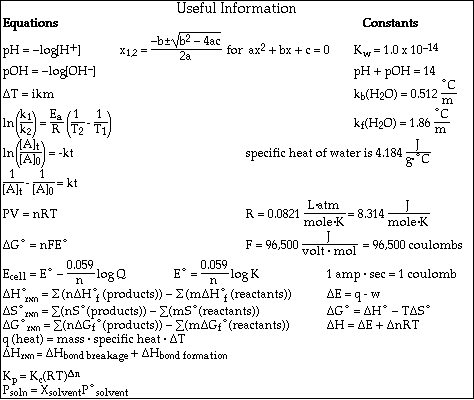
(8) 1. Calculate the molality and the mole fraction of a solution which is 40.0 % HNO3.
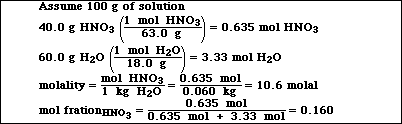
(7) Answer one of the following two problems (#2 or #3).
![]()
2. A 0.550 M solution of NaHCO3 has a density of 1.032 g/mL . Calculate the molality of the solution.
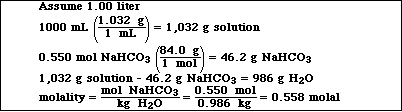
3. A solution of K2CO3 is 0.0205 molal. If the density of the solution is 1.09 g/mL , calculate the molarity of the solution.
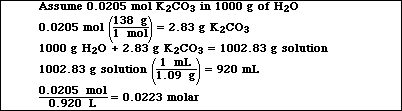
CBS Exam I PAGE 3
(14) 4. The following initial rate data was collected for the reaction;
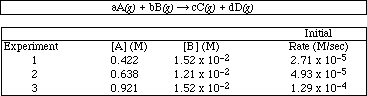
i) Determine the reaction order for A and B.
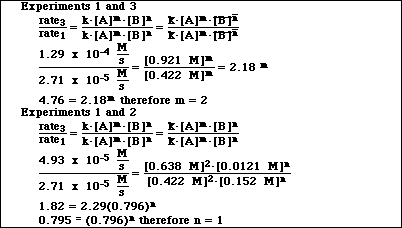
ii) Write the specific rate law for the reaction?
rate = k[A]2[B]1
iii) Determine the rate constant for the reaction (include units).

CBS Exam I PAGE 4
(7) 5. An 18.8 g sample of a nonelectrolyte is dissolved in 125 g of water. The solution freezes at -1.94 ºC. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown compound.
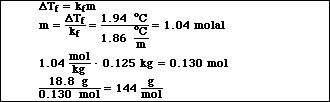
(18) 6. Thionyl chloride, SOCl2, decomposes according to the equation,
![]()
The decomposition is first order with a half-life of 3.2 x 104 seconds at 320 ºC.
a)Calculate the rate constant for this reaction at 320 ºC.
![]()
b)How long would it take 30.0 % of a sample of SOCl2 to decompose?
When 30% of the reactant has decomposed then [A]t = 0.70 [A]0
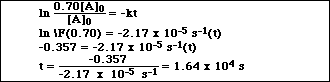
CBS Exam I PAGE 5
c)If the activiation energy for this reaction is 150 kJ, calculate the temperature at which the rate constant is 1.00 x 10-3 s-1.
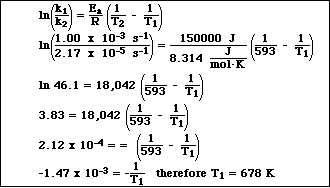
(7) 7. A solution was prepared by mixing 75.0 g of glucose (C6H12O6) in 250. g of water.
Answer one of the following questions related to the solution described above.
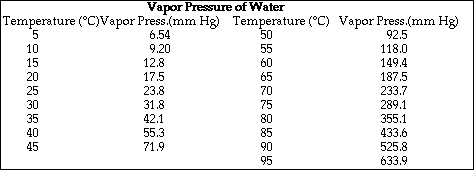
a) Calculate the vapor pressure of water above the solution at 25 ºC.
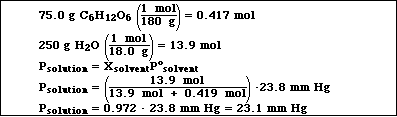
b) Calculate the freezing point and the boiling point of the solution.
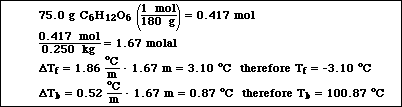
CBS Exam I PAGE 6
(9) 8. Five plots, labeled A) - E) are shown below. Choose any three and briefly explain what information can be obtained from the plot.
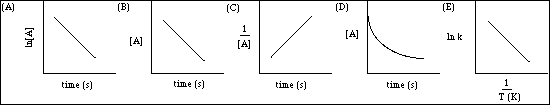
(A) The rate constant for a first order reaction can be obtained from the slope
of the line.
(B) The rate constant for a zero orcer reaction can be obtained from the slope
of the line.
(C) The rate constant for a second order reaction can be obtained from the
slope of the line.
(D) The slope of the line tangent to the curve at t = 0 is the initial rate of the
reaction.
(E) The activation energy can be obtained from the product of the slope of the
line and R.
(9) 9a) Sketch a plot of energy versus reaction path for an exothermic chemical reaction have an activation energy approximately equal to its enthalpy of reaction.
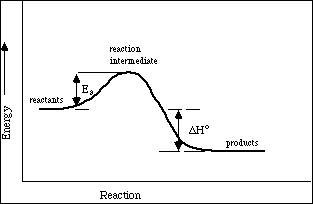
b) Label the diagram in part a). Identify the reactant area, product area, reaction intermediate area, DHºrxn, and Ea.
c) Using a dashed line (------) sketch in the plot of energy versus reaction path when a catalyst has been added to the reaction mixture.
CBS Exam I PAGE 7
d) Explain in a few sentences, referring to your sketch, how a catalyst effects the rate of the chemical reaction.
A catalyst increase the rate of the reaction by providing an alternative pathway for the chemical reaction. The alternative pathway has a lower activation energy.
CBS Exam I PAGE 8
Multiple Choice: (21 points)
Print the letter (A, B, C, D, E) which corresponds to the answer selected.
10. B ![]() 11. C
11. C ![]() 12. A
12. A ![]() 13. E
13. E
14. D ![]() 15. B
15. B ![]() 16. D
16. D
ONLY THE ANSWERS IN THE AREA ABOVE WILL BE GRADED. Select the most correct answer for each question. Each question is worth 3 points.
10. Which of the following solute:solvent pairs will form a solution?
A) CBr4(l):H2O(l)
B) Br2(l):C6H14(l)
C) AgCl(s):H2O(l)
D) I2(s):H2O(l)
11. A solution is prepared by dissolving 12.0 g of sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3, in 1.00 kg of distilled water. The freezing point of the solution is determined to be -0.528 ºC. Which of the following equation best describes how sodium bicarbonate ionizes in water.
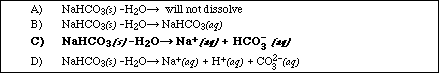
12. Which of the following solutions has the lowest freezing point?
A) 0.100 M CaCl2
B) 0.100 M C6H12O6
C) 0.100 M KCl
D) 0.100 M AgNO3
E) 0.100 M CO2
CBS Exam I PAGE 9
13. Given the following mechanism;
![]()
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The specific rate law for the reaction is; rate = k[NO]2[H2]0
B) The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is 2NO(g) + 2H2(g)  N2(g) + 2H2O(g).
N2(g) + 2H2O(g).
C) N2O2 and N2O are both intermediates in the reaction.
D) The first step of this mechanism is rate determining step.
E) Steps 2 and 3 in the mechanism suggest the overall rate of the reaction will be proportional to the [H2].
14. The diagram below represents a 2-dimensional model of a sample of water at a particular temperature.
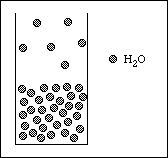
Which of the following diagrams best represents the same system following the addition of a sample of sucrose (C12H22O11)? D
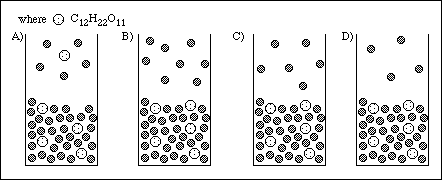
CBS Exam I PAGE 10
15. Which of the following statements is true for simple reactions which follow first order kinetics?
A) The units for the rate constant are M-1·s-1
B) The time required for 75 % of a sample to react is independent of the initial
concentration of reacting species.
C) A plot of concentration versus time is always linear.
D) If the concentration of reacting species is doubled, the rate of the reaction increases by a factor of
four.
E) The rate constant remains unchanged when the temperature changes.
16. Which of the following statements is true for a solid solute with a highly exothermic heat of solution when dissolved in water?
A) The solute is more likely covalent than ionic.
B) The solid has a low heat of hydration (hydration energy).
C) As the solute dissolves, the temperature of the solution decreases.
D) The solubility of the solid increases at higher temperatures.