

1. The solubility of PbCrO4 is 1.34 x 10-7 mol/L at 25ºC. Calculate the value of Ksp.
2. The Ksp for Agcl is 1.7 x 10-10 at 25ºC. What is the solubility of AgCl?
1. Taking both entropy and enthalpy into consideration,
explain why a gas is less soluble in water, whereas certain
solids are more soluble in warm water.
[When a gas dissolves in water it forms weak bonds to the
water and occupies less space. It also has slightly more order
than it would as a free gas. Thus dissolving of a gas is
exothermic (bond forming) and decreases entropy. Solids also
generally dissolve exothermically but become considerably
disordered as they move freely in the water. Since processes are
favored by increased entropy and lower energy, solids tend to
dissolve in water. Gases dissolving are favored by energy but not
by entropy, so lower solubility is expected.]
DG = DH - TDS
DG < 0 if DH
< 0 and DS < 0
(Note that increasing T makes DG
smaller)
2. Refer to the accompanying table of solubility product constants to answer these questions:
a. Although the ionic solids listed in the table are considered insoluble, which compound is the least soluble?
[CdS has the smallest Ksp and is therefore least soluble.]
Which is the most soluble?
[CaSO4 is largest, thus most soluble.]b. Which three compounds are the most insoluble?
[PbS, CdS, ZnS have the lowest Ksp's]
Does this suggest a generalization?
[Sulfides in general have low solubility.]
NOTE: When a different number of ions per mole of slightly soluble salt form, the magnitude of the solubility product constant is not an immediately comparable value to determine relative solubility. For example, the K’s of CaCO3 and CaF2 are 4.95 x 10–9 and 1.61 x 10–10 , respectively, but their molar solubilities are 7.04 x 10–5 and 3.43 x 10–4, respectively.
| Formula | Ksp | Formula | Ksp |
| AgBr | 7.7 x 10-13 | CaSO4 | 6.1 x 10-5 |
| AgCl | 1.7 x 10-10 | MgCO3 | 1 x 10-5 |
| AgCN | 2 x 10-12 | MnS | 1.4 x 10-15 |
| AgI | 8.3 x 10-17 | PbCO3 | 1.6 x 10-13 |
| BaCO3 | 4.9 x 10-9 | PbCrO4 | 1.8 x 10-14 |
| BaSO4 | 1.5 x 10-9 | PbSO4 | 1.9 x 10-6 |
| CdCO3 | 2.5 x 10-14 | PbS | 7 x 10-28 |
| CdS | 1 x 10-28 | SrSO4 | 2.8 x 10-7 |
| CaCO3 | 4.8 x 20 -9 | ZnS | 4.5 x 10-24 |
c. Certain toxic metal ions, including lead and mercury, are
precipitated as a sulfide and then buried in an EPA approved
landfill. Why is this an acceptable way to treat these toxic
substances?
[Because these sulfides have such low solubility it is
unlikely that they would dissolve and leach into the
environment.]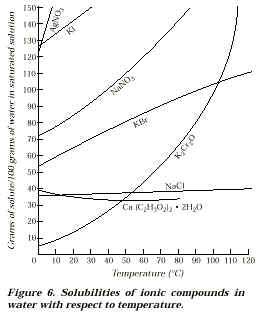
Refer to Figure 6 to answer the following questions:
(page 15, & 16)