5. What is the relationship between the water-soluble vitamins and enzyme
function? Find out which vitamins are related to which enzymes and which
disease or deficiency state results when that vitamin is missing. You can
research this problem in the library. Ask a physician or pharmacist for
advice.
 Enzymes are
proteins. The word protein is from the Greek protos,
meaning ‘‘first,” or
Enzymes are
proteins. The word protein is from the Greek protos,
meaning ‘‘first,” or
Amino acids are compounds containing
both an amino group and a carboxylic acid
group. All amino acids found in proteins
have these two groups on the same carbon
atom.
Of 150 known amino acids, only about 20
commonly occur in human protein. Eight
of these common amino acids cannot be
synthesized by the body and must be
included in the diet. These are called
essential amino acids. All of these amino acids have the basic structure
as shown,
and differ only in the group attached to the carbon atom bearing the amino
and
carboxylic acid groups. Natural amino acids have the L-configuration. Three
typical
amino acids are:
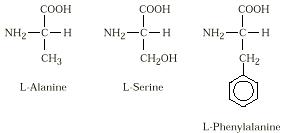
TABLE OF CONTENTS TOPIC OVERVIEW CONCEPT/SKILLS DEVELOPMENT LINKS/CONNECTIONS EXTENSIONS