Functional Group
|
Condensed Formula
|
Name
|
Structure
|
Lewis Structure
|
Comments
|
alcohol
|
CH3OH
|
methyl alcohol
|
|
|
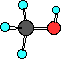
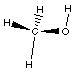
In methyl alcohol, or methanol the red atom is an
oxygen. It has a hydrogen attached to it as well as the
methyl group. Methanol is similar to water, HOH, where
one of the hydrogens is replaced with the methyl group.
The geometry is 'bent' around the oxygen atom in
methanol. Notice the condensed structural formula and the
arrangement of the atoms in the Lewis structure.
|
alcohol
|
CH3CH2OH
|
ethyl alcohol
|
|
|
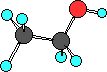
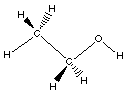
Ethanol is the second alcohol. Both of these two
alcohols are very important and you must be able to draw
their Lewis structures and name them. Notice the
condensed formula CH3CH2OH and the Lewis structure so
you see oxygen atom is bonded to a carbon and a hydrogen.
|
ether
|
H3COCH3
|
dimethyl ether
|
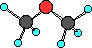
|
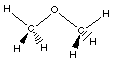
|
Ethers are slightly differnet compared to an
alcohol. Notice in an alcohol the oxygen atom has one
hydrogen atom and the other group is a hydrocarbon. In
ethers both groups attached to the oxygen atom are
hydrocarbon groups. In this case both are methyl groups.
|
ether
|
CH3CH2OCH2CH3
|
diethyl ether
|
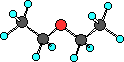
|
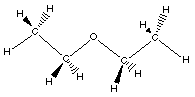
|
Here the hydrocarbons are both ethyl groups.
|
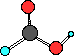
carboxylic acid
|
HCOOH
|
formic acid
|
|
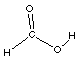
|
In carboxylic acids there are two oxygen atoms.
One of the oxygen atoms has a hydrogen bonded to it like
in the alcohols. The other oxygen atom is double bonded
to the carbon. Look at the Lewis structure. The carboxyl
group is sometime written as -COOH group in the compound.
|
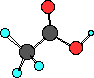
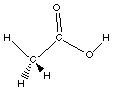
carboxylic acid
|
CH3COOH
|
acetic acid
|
|
|
Acetic acid, a component of vinegar is the first
carboxylic acid with an R- group bonded to the carbon
atom of the carboxyl group. I want you to know this
structure.
|
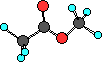
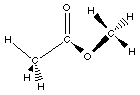
ester
|
CH3COOCH3
|
methyl methyl ester
|
|
|
In esters the hydrogen atom bonded to the oxygen
atom in the carboxylic acid is replaced with an R- group.
|
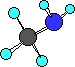
amine
|
CH3NH2
|
methylamine
|
|
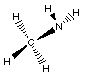
|
The blue atom is the nitrogen atom. Notice in
methylamine the carbon atom of the methyl group is bonded
to the nitrogen. In amines the nitrogen atom alway has
three bonding groups and one lone-pair.
|
amine
|
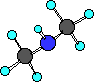
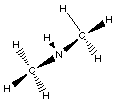
(CH3)2NH
|
dimethylamine
|
|
|
In this example of an amine two R- groups are
bonded to the nitrogen.
|
amine
|
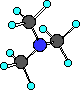
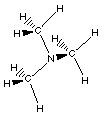
(CH3)3N
|
trimethylamine
|
|
|
In this example of an amine three R- groups are
bonded to the nitrogen.
|
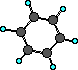
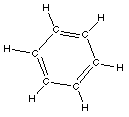
aromatic
|
C6H6
|
benzene
|
|
|
Aromatics are rings
with carbon atoms with alternating single and double
bonds.
|