Ester Functional Group
Esters are very similar to carboxylic acids. The carboxylic
acid functional group is shown along with the ester functional
group.
Functional Group
|
Lewis Structure
|
Electron-dot Structure
|
Condensed Formula
|
Carboxylic acid
|
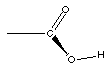
|
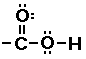
|
-COOH
|
Ester
|
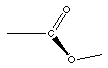
|
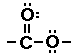
|
-COO-
|
The ester functional group does not look much differet next
to the carboxylic acid functional group. In fact you might notice
the only diference is the hydrogen atom, present in the
carboxylic acid absent in the ester. This IS the key difference.
So what does the ester have in place of that hydrogen atom? Ester
have carbon atoms in place of that hydrogen.
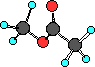
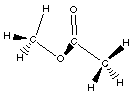
The simplest ester is H3CCOOCH3. The
structure of this compound is shown below.
Ball-and-Stick
|
Lewis Structure
|
Electron-dot Structure
|
|
|
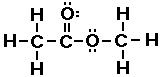
|
So esters have a carbon atom attached to the oxygen that a
hydrogen atom is attached to in a carboxylic acid.
So for both the ester and the carboxylic acid we look for a
carbon atom with one double bonded oxygen and one single bonded
oxygen. The difference between the ester and the carboxylic acid
is whether the single bonded oxygen has a hydrogen atom bonded to
it or a carbon atom.
Esters have very pleasant odors. The odors of the three
esters below are very familiar to all of us.
Return
to man functional group page.