
WITHIN CHEMISTRY
- Organic Functional Groups. Structurally,
many drugs are carboxylic acids, alcohols, amines, esters, ethers, aldehydes, and/or
ketones.
Examples are:
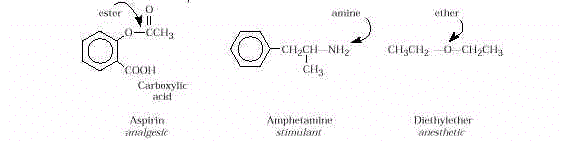
- Nomenclature. Several names can be used to specify a drug. Generic
names are often used. The brand name (or trademark name) is the name adopted for use by
the drug company that markets the drug. Each company chooses its own trade name. There is
only one generic name for each drug, but there may be many brand names. For example,
acetaminophen (generic name) is sold as Tylenol, Tempra, Datril, Liquiprin, and Trilium
(brand names). Drugs are also referred to by street names (see Drug Reference Chart inTips
for the Teacher section).
- Acids and Bases. Pain sensation arises from a response of nerve endings
to a change in pH of solutions around them. Neutralization of the solution in the tissues
that is causing the irritation or pain relieves the pain. Certain organic functional
groups are responsible for the acidic or basic properties of these substances. For
example, lidocaine, a local anesthetic used by dentists, containsabasicamino
group.Tominimizethe localirritationanddiscomfort when lidocaine is used, it is
administered as a neutral salt solution.

- Extraction. Many of the active ingredients
in plants contain basic nitrogen atoms and can be extracted from the bulk of the plant
material by dilute acid. Because these compounds behave similar to an alkali, they are
referred to as alkaloids.
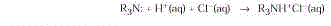
After extraction, free alkaloids
can be regenerated by treatment with aqueous base.
Cocaine, morphine, and atropine
are obtained in this way.
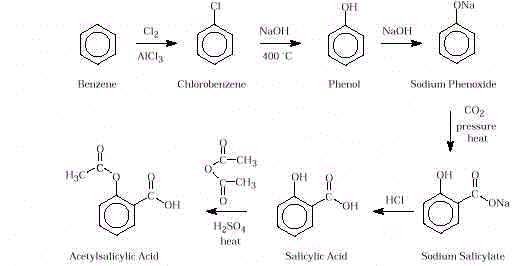
- Synthesis. Drugs that do not occur
naturally in plants or animals must be synthesized in the laboratory. Many naturally
occurring drugs are also synthesized to increase cost effectiveness and supply. Although
salicylic acid is a good analgesic and antipyretic, it is sour and irritating when taken
orally. Chemists modify the molecule’s structure to remove this undesirable property
while retaining the desirable medicinal property. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) is
prepared from salicylic acid by treatment with acetic anhydride (see Activity 1).
Salicylic acid is made from benzene, which is obtained from coal tar.
- Structure-Activity Relationships. Chemists
have determined the structures of many naturally occurring biologically active compounds.
Such information is useful in relating pharmacological action to chemical structure within
a group of compounds with similar action.
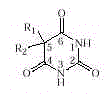
Barbiturates contain the ring structure shown. Variation of the R groups at C-5 can modify
the sedative-hypnotic action. For example, incorporating a phenyl group
(C 6 H 5 –) yields a barbiturate that
is less water soluble and more resistant to biodegradation and is therefore longer acting.
Researchers can synthesize many
different barbiturates
and select those with the greatest promise.
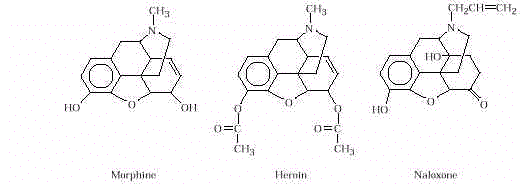
The analgesic properties of morphine
are due to the presence of hydroxy, ether, and amine groups that help bind it to the
receptor site. Heroin is easily converted in
the human body to morphine in an
enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of the two ester (CH 3 COO–)
groups. Naloxone is a narcotic antagonist. By changing a hydroxy
group to a ketone (–C=O), a
methyl group to an allyl group (–CH 2 CH=CH 2 ), introducing another hydroxy group, and by reducing a
double bond, the drug still fits
the opiate receptor sites in
the brain but has lost all of its narcotic and respiratory depressant activity.
In
another example, cancer has been successfully treated using the structure-activity
relationship. Mercaptopurine is similar to the real metabolite adenine.
Rapidly growing
cancer cells can mistake mercaptopurine for adenine. Mercaptopurine is an analog of
hypoxanthine from which adenine is synthesized. When
this
molecule is incorporated as a "useful" metabolite into cancer cells, cell growth
is impeded. Mercaptopurine is called an antimetabolite. Although effective in
cancer
treatment, anti-metabolites also harm normal cells.

- S t e r e o c h e m i s t r y.
Benzedrine’s active ingredient is the dextrorotatory form in a racemic mixture.
Cisplatin is only an active chemotherapeutic in the cis-form. Transplatin has no
therapeutic effect. These steric effects are a special case of structure-activity
relationships.
- Instrumentation and diagnosis. Magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) is a technology based on the same principle of operation as a
nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer used by chemists in structure determination (see
Instrumentation module). The MRI scans the individual without exposing the patient to
X-rays (as in CT scan) or gamma radiation (as in PET scan). In MRI, a low energy radio
frequency wave interacts with the hydrogen atoms in water molecules in soft tissue. The
energy produced from this interaction is fed into computers that produce an image similar
to that of CT and PET scans. MRI has proved to be useful for studying soft tissue (tumors,
cancerous tissue, the pelvic area, prostate gland, and bladder). Use of this technique has
improved the diagnosis of cancer in these soft tissues.
BETWEEN CHEMISTRY AND OTHER DISCIPLINES
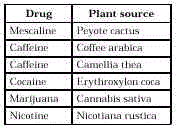
- Botany. Plants are an important
source of drugs. Many of these drugs are legal, but some are drugs of abuse. Plants were
used by early humans in religious rituals (peyote), medically (to treat diarrhea or worm
infestation), and as poisons (Socrates’ cup of hemlock tea that contained the active
ingredient coniine).
Examples of plant-source drugs in use today are shown here.
2. Pharmacology. When a drug is administered
orally, it follows the pathway shown here:
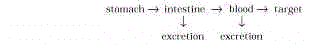
When a drug is administered by
injection into fat or muscle tissue, the intestinal tract is not involved, and the drug
finds its way into the blood stream and then to
its target. The
mechanisms by which some drugs functionare summarized below:
- Analgesics and antipyretics. These drugs inhibit the synthesis of
prostaglandins that are responsible for perception and a rise in body temperature.
- Local anesthetics. These drugs block nerve impulses to the brain.
- Morphine, codeine, and meperidine. Receptor sites in the brain accept
naturally produced substances released as a response to pain (enkephalins). Morphine,
codeine, and meperidine have structures that are similar to the enkephalins and can fit
the brain’s receptor sites. The better the fit, the better the analgesic action. Note
the structural similarity (circled areas) in each structure, as shown.

- Amphetamines in weight control . An excited or angry person secretes
extradopamine and norepinephrine.These are then distributed to the brain and intestinal
tract. The central nervous system is stimulated, and digestion of food is temporarily
halted to the extent that interest in food and eating is lost. Because amphetamines are
structurally similar to these two body chemicals, they produce the same kind of intestinal
tract suppression.

- Alcohol. A liver enzyme causes the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde
(CH 3 CHO), then to acetic acid (CH 3 COOH), and finally, to CO 2 . The
"belch"associated with drinking beer is due to the build up and release of
carbon dioxide in the beer (see Links and Connections within Chemistry in the Organic
Chemistry module for additional discussion of alcohol metabolism).
- Alkylating agents. These agents transfer alkyl groups to guanine, a
nitrogen base in DNA, blocking base pairing and preventing DNA replication. Healthy cells
are harmed as well. (Alkylating agents are used in the treatment of cancer.)
- Antimetabolites. These agents interfere with DNA synthesis by
inhibiting the formation of thymine-containing nucleotides. (Antimetabolites are used in
the treatment of cancer.)
- Penicillins. Penicillins prevent cross-linking in the formation
ofbacterial cell walls. Human cells are of a different chemical composition and are not
affected.
- Birth control pills. The synthetic progesterone blocks the release of a
hormone that stimulates the ovaries to release an egg. If an egg isn’t released,
pregnancy is impossible.
3. Biochemistry. Nearly all the drugs we take are
foreign to the body. The process by which the body accepts a drug, alters it chemically to
eliminate the drug
action, and
then prepares it for excretion is called metabolism. The product of chemical breakdown of
a drug is called a metabolite. Drug metabolism occurs
primarily
in the liver. The liver changes a drug chemically so that the metabolite is more soluble
in the aqueous medium of the urine. Chemically,these processes
involve
hydrolysis, attachment to a normal body substance, oxidation, or salt formation. For
example, the local anesthetic procaine (Novocain) is hydrolyzed to
p-aminobenzoic
acid, which has no anesthetic effect but, more importantly, is more water soluble
than procaine.

- Genetics. In any population, there are individuals who are sensitive to
a given drug and those who are resistant. The resistance is imparted by the genetic
composition of the individual. Resistance to antibiotics by certain microorganisms is an
example of this phenomenon. Broad spectrum antibiotics have been developed to encompass a
greater number of the resistant population.
TO THE CONTEMPORARY WORLD
Community
Knowledgeable individuals: pharmacists, nurses, physicians, hospital directors, drug
unit in a police department Societal (Science/Technology/Society; current events)
- Drug dependence. Dependence is a situation in which drug users develop
reliance, either physical or psychological. Tolerance and withdrawal are not necessarily
seen. For example, cocaine induces a psychological dependence, but does not induce the
development of tolerance. (Addiction is a drug-induced change in the physical state of an
individual characterized by a development of tolerance and withdrawal syndrome).
- Drug testing in Olympic games. Drug testing is an integral part of the
Olympic Games. The International Olympic Committee uses instrumentation (primarily gas
chromatography and mass spectroscopy) to detect drug use prior to an athlete’s
competition. The first four finishers plus one random competitor provide a urine sample
within 1 hr of the competition’s end. Drugs that have been banned include
amphetamines, narcotics, analgesics, anabolic steroids, diuretics, and beta blockers.
Athletes must be careful not to use cold medicines that contain ephedrine,
pseudoephedrine, or phenylpropanolamine as these drugs could give false positive tests for
amphetamines. Some anabolic steroids can be detected months after the last use;
termination just before a competition will not normally avoid detection.
- Drug testing in the workplace. Reduced productivity due to alcohol and
drug abuse costs the federal government and society in general billions of dollars each
year. Drug use on the job can result in accidents, absenteeism, health problems, memory
loss, turnovers, and loss of skills and coordination. Such problems have caused segments
of government and private industry to institute drug testing. Alcohol and marijuana are
drugs commonly abused, but amphetamines, barbiturates, cocaine, and opiates are also
abused. If an individual is a government employee, the employer must have probable cause
before the individual can be tested. Private employers have the right to demand drug tests
at hiring time.
- Drug equivalence. Unless the physician has prohibited substitution of a
generic drug for a brand name drug, pharmacists may substitute a less expensive generic
drug. In many cases, generic name drugs cost one-fourth as much as their brand name
equivalents. The concern for the consumer is the equivalency in effectiveness of the
generic drug. Studies have shown that differences in absorption of brand name and generic
drugs into the bloodstream are very small.
- Drug design versus designer drugs . Designer drugs are substances
contrived in illegal laboratories to be chemical analogs of well-known controlled
substances. Their slight difference in chemical structure renders them outside the
jurisdiction of the law. Shown here is the structural relationship between the narcotic
analgesic Fentanyl and its analog, a-methylfentanyl.

The minor structural change does not alter the fundamental analgesic nature, but a-methylfentanyl is a more powerful narcotic than Fentanyl.
Many of today’s
designer
drugs were synthesized years ago by legitimate medical researchers but rejected because of
serious adverse effects.
Drug design, on the other hand, is the synthesis and study
of legal substances to treat a particular disease or condition. Chemists have designed
molecules to
relieve headaches, cure infectious diseases, prevent conception, and kill cancer cells
(see examples in Tips for the Teacher section).
Salicylic acid, extracted from willow bark, was found to be
useful in reducing fever and pain. However, it is sour and irritating when taken orally.
Chemists sought to modify the structure of the molecule to remove this undesirable
property while retaining and improving the desirable properties. The first modification
was neutralization of the acid. The salt, sodium salicylate, was less unpleasant to
swallow, but it was highly irritating to the stomach lining. Phenylsalicylate, the next
substitute, passed unchanged through the stomach. In the small intestine, it was
hydrolyzed to the desired salicylic acid, but phenol that israthertoxic, was also formed.
Acetyl salicylic acid (aspirin) was then introduced.
Thus a knowledge of the structure of drug molecules enables
chemists to be more efficient when they design drugs. A knowledge of the structure of the
drug molecule is not sufficient for an understanding of the molecular basis of the
drug’s action, however. It is also necessary for chemists to understand the structure
of the molecules of the human body, of bacteria, and of viruses.

- Role of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The FDA is responsible for approving the marketing of all new drugs sold in the U.S. The
FDA also monitors drug use after approval. It can take up to ten years for a new drug to
pass the rigorous program of safety and effectiveness for its intended use. First,
evidence must show that the new drug has therapeutic activity in animals, that it shows
promise for human use and that it appears to be safe for human testing. This is followed
by human testing in patients with the disease and can involve thousands of patients to
determine the drug’s safety and effectiveness. Finally, the FDA examines all the
evidence of safety and effectiveness and decides whether the drug will be approved for
marketing. The FDA is very cautious so that people will be spared anguish and needless
suffering.
- Drug interaction. The interaction of drugs
with each other to heighten each drug’s effect is called synergism. The effects can
be helpful or harmful. Physicians have succeeded in prolonging the lives of some cancer
patients with combinations of drugs. When the drugs are given in combination, lower doses
of each drug can be used, and the harmful side effects of chemotherapy reduced. On the
other hand, alcohol (a depressant) increases the action of many antihistamines and
tranquilizers (depressants) resulting in a superdespondent, dangerous combination.
- Drug manufacture. Drug manufacture today is
classified into five groups according to primary source. Plant extracts give alkaloids
such as opium, quinine, atropine, and the precursors of steroid drugs. Animal extracts
provide insulin and hormones. Vaccines and serums are prepared using biological sources.
Fermentation is used for antibiotics such as penicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline, and
steroid modification. Synthetic chemistry produces aspirin, tranquilizers, and
antihistamines.
- Drug delivery. Drugs can be administered
through one of the following routes: oral ingestion, inhalation, injection, body orifices,
skin application, skin patch, implants, and microsponges. Most drugs are taken orally.
They dissolve in the stomach acid and enter the blood stream by absorption from the
stomach or intestine. Inhaled drugs are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream. Nasal
decongestant sprays work by shrinking the nasal membranes. Injection also provides a
direct route to the bloodstream, eliminating the possibility of undesirable taste or
destruction by digestive juices. Drugs can also be administered in the form of eye drops,
eye inserts, under the tongue tablets, and rectal and vaginal inserts. Smokeless tobacco
users get their nicotine by stuffing tobacco between the gum and the cheek. Medications
can be applied to the skin as ointments or as aerosol sprays. Skin patches are worn on a
convenient area of the body as the drug is slowly absorbed into the bloodstream. One such
skin patch releases scopolamine to the bloodstream and provides prolonged protection from
the nausea and vomiting of motion sickness.
Surgical implantation of a drug (pellet, reservoir, or pump) is another method of drug
delivery. Contraceptive drugs have been implanted under the skin of a woman’s
upper arm. These
implants, consisting of long, thin silicone rubber capsules that contain the drug, slowly
release the contraceptive drug for about five years.
Microsponges can
be programmed to release drugs in response to pressure, time, or temperature changes. For
example, a foot powder could release more
antifungal drug
with each step.
- Folk medicine. This type of medicine is
part of the culture of a geographical people, such as the American Indians. Folk medicine
deals with the emotional needs of the patient that may be related to the
patient’s bodily ailments. The Native American medicine man often involved a
patient’s family and tribe so that personal conflicts
were resolved while the patient also recovered physically. The tribal members sometimes
offered gifts to the patient, and sometimes the ritual involved a
family member with whom the patient had quarreled.
Many practices of folk
medicine are based on religion, superstition, or social customs. The medical (and
religious) value of coca leaves was well recognized
by the Incas. It was
not until the 19th century that its analgesic property was recognized as due to cocaine.
On the other hand, gold has no therapeutic value in the
treatment of jaundice.
The indigenous peoples of North America thought, erroneously, that "like cures
like," and the color of gold matched that of the jaundiced
person. With the
various flora around them, they had a variety of remedies. They used foxglove as a remedy
for fluid build-up in the legs resulting from heart failure.
Today, the active
ingredient in foxglove, digitalis, is a powerful cardiac drug. Native American medicines
found their way into early folk practices of the white
settlers.
Unscrupulous peddlers claiming to have learned tribal formulas began to sell secret
potions and elixirs. Many were nothing more than placebos and
alcohol.
Traveling road shows sold patent medicines such as Wigwam Tonic.
There are over 200 indigenous
drugs used by the Native Americans. Some of the common native North American plants that
were (or still are) used medically are
bloodroot (causes vomiting),
podophyllum (for warts), tobacco (for toothache), goldenseal (an astringent), and mint
(for fevers). Folk medicine is still practiced on
some reservations.
- Holistic medicine. Holistic medicine involves an understanding of the
patient’s whole situation. Emotional, spiritual, social lifestyle, and environmental
factors are considered in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. Many holistic
approaches rely on psychology, and some practitioners emphasize muscular alignment
through music, personal awakening, and physical manipulation. The
importance of the mind in the treatment of physical ailments cannot be underestimated.
- Acupuncture. This Oriental practice has been shown to relieve the
symptoms of certain ailments or diseases. While its mechanism is not understood,
its effectiveness is thought to be based on
stimulus of endorphin synthesis in the body.
- Have you recently had a headache? In North America, about 40 million pounds of aspirin
is consumed per year. Since the average dose of two tablets is 1.7 X 10 –3 mol, the total amount consumed corresponds to 59 billion
headaches. That’s enough to give anyone a headache!
- The nicotine in the smoke inhaled from a pack of 20 cigarettes ranges from 2.0 to 40 mg!


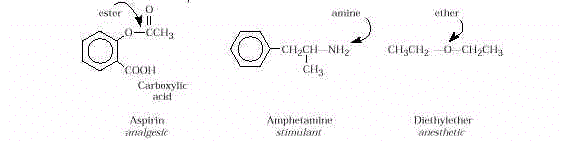

![]()
![]()



![]()




