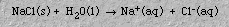
1.Ions
b. An electrolyte is a substance that, in water solution, is capable of conducting an electric current. An aqueous solution of sodium chloride conducts an electric current; therefore NaCl is an electrolyte. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that does not dissociate into ions in solution and therefore does not conduct an electric current. Sugar is a nonelectrolyte.
c. Ionization of covalent substances is the breaking apart of a covalent substance into ions in aqueous solution. Hydrogen chloride ionizes completely in aqueous solution into hydrogen ions and chloride ions and is thus classified as a strong acid. Acetic acid only slightly ionizes in water; it is a weak acid.
d. Dissociation is separation of an ionic substance into ions in an aqueous solution. For example, sodium chloride, NaCl, dissociates as follows:
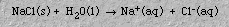
2.Solution Concentration. The molarity or molar concentration (M) of a solution is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. A solution of 20.0 g sodium hydroxide, NaOH, in one liter of solution has a concentration of 0.500 mol/L NaOH, or 0.500 M NaOH.
3. Classification and identity of some common acids and bases.
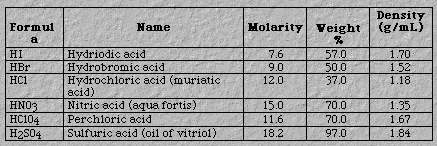
Weak acids. Unless otherwise informed, one can assume other common acids are weak. Figure 4 presents two examples:
 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS | TOPIC OVERVIEW | CONCEPT/SKILLS DEVELOPMENT | LINKS/CONNECTIONS | EXTENSIONS |  |
|---|