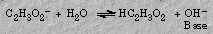
Similarly, ammonium chloride forms an acidic solution because only the cation hydrolyzes:
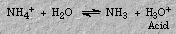
Sodium acetate forms a basic solution because the acetate ion reacts with water to form hydroxide ion:
Similarly, ammonium chloride forms an acidic solution because only the cation hydrolyzes:
Suggested Demonstration
A buffer is a system that maintains a nearly constant pH in a solution when relatively small amounts of acid or base are added to the solution. A buffer is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid.A buffer can be prepared by mixing a weak acid (for example, carbonic acid, H2CO3) with one of its salts (for example, sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3), since the anion (HCO3-) of the acid is the conjugate base. This buffer is very important in maintaining a nearly constant pH of the blood. A weak base (NH3) mixed with one of its salts (NH4Cl) can also function as a buffer.
 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS | TOPIC OVERVIEW | CONCEPT/SKILLS DEVELOPMENT | LINKS/CONNECTIONS | EXTENSIONS |  |
|---|