A titration is performed using by adding 0.100 M NaOH to 40.0 mL of 0.1 M
HA (Ka is 1.0 x 10-5.).
d) Calculate the pH at the equivalence point.
Answer:
The equivalence point is the point in the titration where;
moles of base (NaOH) = moles of acid (HA)
Since we are adding the base to the acid, we know how many moles
of acid are present;
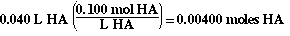
We need the same number of moles of base (NaOH) at the equivalence
point;
0.00400 moles NaOH
So the 'ICE table' now looks like;
|
NaOH(aq)
|
+ HA(aq)
|
--->
|
NaA(aq)
|
+ H2O(aq)
|
I
|
0.00400 mol
|
0.00400 mol
|
|
0
|
-
|
C
|
|
|
|
|
|
F
|
|
|
|
|
|
Since K for the reaction is large, the reaction will go to
completion. This means that the reactant in the smallest amount will completely
react. At this point in the titration there are fewer moles of base compared
to acid. So all the base reacts. Adding this to the 'ICE table' we have;
|
NaOH(aq)
|
+ HClA(aq)
|
--->
|
NaA(aq)
|
+ H2O(aq)
|
I
|
0.00400 mol
|
0.00400 mol
|
|
0
|
-
|
C
|
-0.00400 mol
|
-0.00400 mol
|
|
+0.00400 mol
|
-
|
F
|
|
|
|
|
|
The final amount of each species can be obtained just as it
always has been in the other ICE tables, by adding the change to the initial
amount.
|
NaOH(aq)
|
+ HA(aq)
|
--->
|
NaA(aq)
|
+ H2O(aq)
|
I
|
0.00400 mol
|
0.00400 mol
|
|
0
|
-
|
C
|
-0.00400 mol
|
-0.00400 mol
|
|
+0.00400 mol
|
-
|
F
|
0
|
0
|
|
+0.00400 mol
|
|
Focusing on the Final row there is only salt present. This
is the salt of a weak acid and aa strong base. Such a salt does effect the
pH of the solution. We know salts of weak acids and strong bases completely
dissociate in water to form the cation and anion,
NaA(aq) ----> Na+(aq) + A-(aq)
The ion Na+ does not effect the pH of the solution,
however A- will effect the pH of the solution. A- is
a weak base (the conjugate base of the weak acid HA). So we must calculate
the pH of this salt. To do that we must write the equation describing how
A- behaves as a base and set up the ICE table for the salt;
|
A-(aq)
|
+ H2O(aq)
|
--->
|
HA(aq)
|
+ OH-(aq)
|
I
|
|
|
|
|
|
C
|
|
|
|
|
|
F
|
|
|
|
|
|
The initial [A-] is calculated by dividing the moles
of A- by the volume of the solution;

Substituting into the ICE table and completing the ICE table;
|
A-(aq)
|
+ H2O(aq)
|
--->
|
HA(aq)
|
+ OH-(aq)
|
I
|
0.0500 M
|
-
|
|
0
|
~ 0
|
C
|
- x
|
-
|
|
+ x
|
+ x
|
F
|
0.0500 - x
|
-
|
|
+ x
|
+ x
|

We can see this point on the titration curve (as point 1d).
