 Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index Go to Main Index
Go to Main Index
Name ________________________
AP Chemistry By Satellite
John I. Gelder
Exam I
February 6, 1992
![]()
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. This examination consists of a total of 9 different pages. The last page includes important mathematical equations, a periodic table, and a table of vapor pressures for water. All work should be done in this booklet.
2. PRINT your name, high school, teaching partner's name and today's date now in the space at the top of this sheet. DO NOT SEPARATE THE PAGES.
3. Answer all questions that you can and whenever called for show your work clearly. Your method of solving problems should pattern the approach used in lecture. You do not have to show your work for the multiple choice or short answer questions.
4. No credit will be awarded if your work is not shown in problem 1, 3, 4 and 5. Please circle your final answer!
5. Point values are shown next to the problem number.
6. Budget your time for each of the questions. Some problems may have a low point value yet be very challenging. If you do not recognize the solution to a question quickly, skip it, and return to the question after completing the easier problems.
7. Look through the exam before beginning; plan your work; then begin.
![]()
8. Relax and do well.
![]()

APCBS Exam I PAGE 2
(18) 1. A solution is prepared by dissolving 25.0 g KNO3 in 200. g H2O. (Molar mass of KNO3 = 101 g/mol )
a) Calculate the weight percent KNO3 in the solution.
![]()
b) Calculate the molality of the solution in terms of KNO3.

c) Calculate the mol fraction of KNO3 in the solution.

d) Identify the ions formed when KNO3 dissolves in water
![]()
![]()
e) Calculate the freezing point of the solution.

APCBS Exam I PAGE 3
(10) 2. Considering intermolecular attractive forces, explain why hexane, C6H14, dissolves in CCl4 but does not dissolve significantly in H2O.
Hexane and carbon tetrachloride both consist of nonpolar molecules. Nonpolar compounds experience only London Dispersion forces.
Water molecules are polar and can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules.
Because hexane and carbon tetrachloride have similar attractive intermolecular forces, their molecules can mix readily, and hexane dissolves in carbon tetrachloride.
Hexane cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. Water molecules experience much more attraction to one another than they do to hexane. Water molecules and hexane molecules cannot mix readily, and thus hexane is insoluble in water.
(10) 3. Answer ONE of the following questions related to laboratory.
A. The freezing point of pure cyclohexane was measured and found to be 6.5 ºC. 0.602 g of acetic acid (CH3COOH) were dissolved in 25.0 g of cyclohexane. The freezing point of the solution was -1.6 ºC.
What is the value of Kf for cyclohexane?
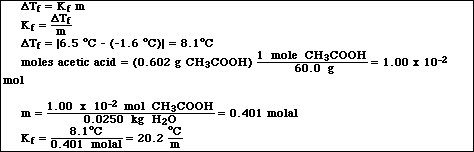
B. If 0.602 g of acetic acid (CH3COOH) were dissolved in 25.0 g of water, Kf = 1.86 ºC/molal the measured freezing point is -0.85 ºC. Calculate the theoretical freezing point of the solution. Compare your answer to the measured value. Explain any discrepancy.

The theoretical freezing point is lower than the observed freezing point. If the observed freezing point depression was twice the theoretical value we could conclude that acetic acid was a strong electrolyte. Since the observed lowering is less than twice the theoretical lowering, we must conclude that acetic acid is partially dissociated in solution. It is a weak electrolyte.
APCBS Exam I PAGE 4
(16) 4. The following initial rate data was collected for the reaction at 45.0 ºC;

a) Determine the reaction order for ClO2 and F2.

b) Write the specific rate law for the reaction?
rate = k [ClO2]1 [F2] 1
c) Determine the rate constant for the reaction (include units).

d) Calculate the initial concentration of F2 in Experiment #4.

APCBS Exam I PAGE 5
e) Calculate the rate of decrease of F2 in Experiment #1.

(18) 5. Molecules of butadiene, C4H6, are known to "dimerize" according to the equation
![]()
This dimerization reaction is second order and the rate constant has a value of 0.0140 M-1·s-1 at 500 ºC.
a)Calculate the concentration of C4H6 after 45.0 seconds if the initial concentration of C4H6 is 0.0250 M.

b)Calculate the half-life for the reaction when the initial concentration of C4H6 is 0.0250 M.

APCBS Exam I PAGE 6
c)What is the activation energy for this reaction if the rate constant at 512 ºC is twice the rate constant at 500 ºC?

(8) 6. When the temperature is below 500 K, the reaction between nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide can be described by the equation,
![]()
The rate equation for the reaction at these temperatures is,
![]()
rate = k[NO2]2
a) Which of the following mechanisms agrees with the experimentally obtained rate equation?

Mechanism #2 agrees with the experimental rate equation.
b) Briefly, explain how you arrived at your choice in part a).
All three of the mechanisms given sum to yield the overall balanced equation. However, according to the experimental rate equation, rate = k[NO2] 2 , the slow or rate determining step in the mechanism must involve a bimolecular collision of NO2 molecules. Only Mechanism #2 has the collison of two NO2 molecules as the rate determining step.
APCBS Exam I PAGE 7
Multiple Choice: (20 points)
Print the letter (A, B, C, D, E) which corresponds to the answer selected.
7. A ![]() 8. E
8. E ![]() 9. C
9. C ![]() 10. A
10. A ![]() 11. D
11. D
12. B ![]() 13. D
13. D ![]() 14. C
14. C ![]() 15. A
15. A ![]() 16. B
16. B
ONLY THE ANSWERS IN THE AREA ABOVE WILL BE GRADED. Select the most correct answer for each question. Each question is worth 2 points.
7. What would be the effect on the measured value of DTf if two nonvolatile solutes dissolved in a solvent
react according to the equation A + B  C? (A,B, and C are covalent compounds.)
C? (A,B, and C are covalent compounds.)
A. DTf would be half as large as expected.
B. DTf would be twice as large as expected.
C. DTf would not be changed by the chemical reaction.
D. DTf would depend on the actual identity of A, B, and C.
E. DTf would be zero.
8. Which of the following does not affect the rate of a chemical reaction?
A. Concentration of reactants
B. Temperature
C. Catalyst
D. Surface area of solid reactants
E. Enthalpy of reaction
9. Which of the following statements is true?
A. The rate of a first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of reactant.
B. The rate of a second order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of reactant.
C. The half-life of a first order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of
reactant.
D. The half-life of a second order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of reactant.
E. The half-life of any chemical reaction is independent of the initial concentration of reactant.
10. Osmotic pressure is
A. the pressure required to prevent osmosis.
B. the pressure required to cause osmosis.
C. the pressure exerted by solvent molecules on a semipermeable membrane.
D. the pressure exerted by solute particles that cannot pass through a semipermeable membrane.
E. the vapor pressure above a solution in contact with a semipermeable membrane.
APCBS Exam I PAGE 8

A. 100. grams
B. 50.0 grams
C. 37.5 grams
D. 25.0 grams
E. 0 grams

12. This plot shows that the chemical reaction is first order. B
13. The activation energy can be determined using this plot. D
14. The slope of this line is equal to the second order rate constant. C
15. The reaction represented by this plot cannot be first or second order. A
16. Suppose a student prepared two solutions, each containing the same amount of solute. The first solution contained 10 g of solvent and the second contained 12 g of solvent.
A. The first solution would have a higher freezing point than the second.
B. The first solution would have a higher boiling point than the second.
C. The first solution would have a higher vapor pressure than the second.
D. Choices A, B, and C are all correct.
E. Both choices A and C are correct.